Dental implants are artificial structures that a dental surgeon inserts into a person’s jawbone. A person may need an implant if they have lost one or more teeth.
Keep reading to learn about the types of implants and associated risks. We also describe what to expect from dental implant surgery and how much the procedure may cost.
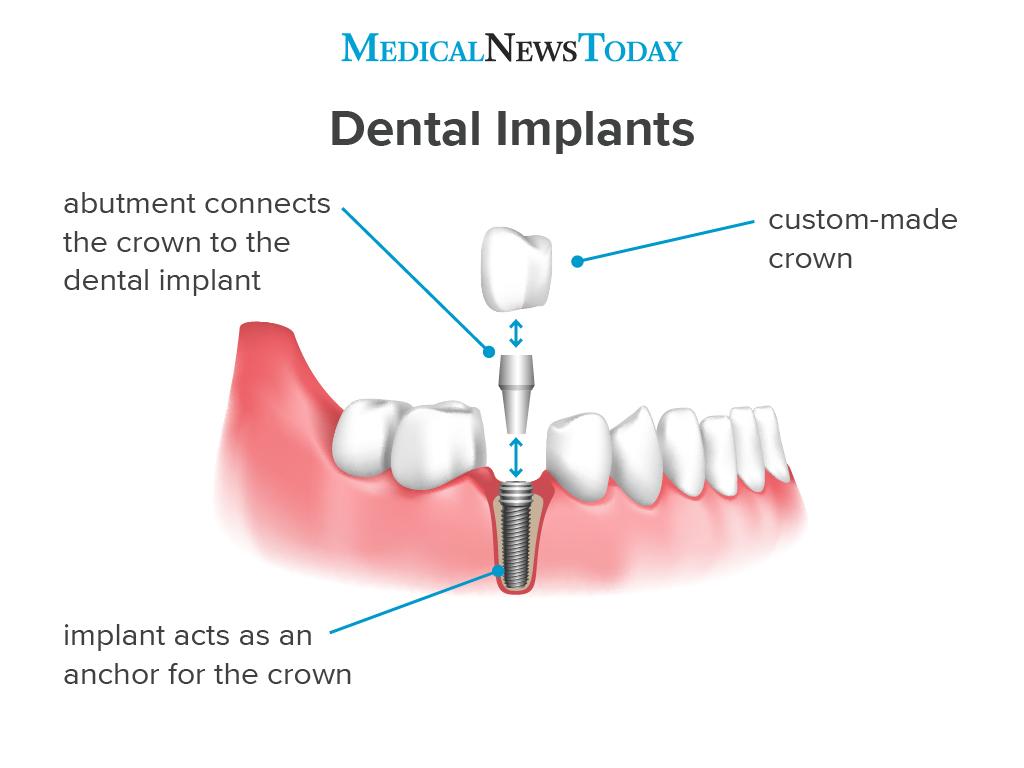
A dental implant is a structure that replaces a missing tooth. With screw-like devices, the surgeon inserts an implant into the jawbone, and it acts as an anchor for an artificial tooth, called a crown.
A device called an abutment connects the artificial tooth to the dental implant.
The crown is custom-made to fit the person’s mouth and match the color of their teeth. Crowns look, feel, and function like natural teeth.
Implants have several advantages over dentures, which are removable artificial teeth. Implants:
- are more natural and comfortable
- have a higher success rate
- improve chewing function
- lead to a lower risk of cavities developing in nearby teeth
- lead to better maintenance of bone at the site of the lost tooth
- cause decreased sensitivity in nearby teeth
- do not need to be taken out and cleaned every night
However, dental implants are not suitable for everyone. The implanting devices must bond with the jawbone, so a person’s bones must be healthy before they can undergo implant surgery.
There are two types of dental implant: endosteal and subperiosteal.
Endosteal implants are the most common type. A surgeon embeds them in the jawbone, and each can hold one or more artificial teeth.
A surgeon affixes a subperiosteal implant on top of the jawbone. Dental surgeons choose this option for people who do not have much height to their jawbone.
According to the American Academy of Implant Dentistry, around 3 million people in the United States have dental implants, and this number increases by about 500,000 every year.
Dental implant surgery is safe when a qualified and experienced surgeon or dentist performs it. It is also the only dental restoration option that maintains the health of the person’s jawbone and stimulates its growth.
Some people are not eligible for dental implant surgery. It is not safe for dental surgeons to operate on people with:
- acute illness
- uncontrollable metabolic disease
- bone or soft tissue disease or infection
If these issues are resolved, a person can have the surgery.
In some cases, dental surgeons refrain from operating on people with:
If people with any of the above undergo dental implant surgery, there is a higher risk of the implant failing.
Dental surgeons may also choose not to operate on people undergoing the following treatments, due to an increased risk of implant complications:
People who undergo this procedure may experience complications during or afterward. The issues may include:
- nerve damage, resulting in altered sensation in the surgical area
- an opening of the incision following surgery
- movement of the implant
- exposure of the implant above the gumline
- infection of the implant
People who experience movement or exposure of the implant may need to undergo additional procedures to improve the health of the bone and gums or remove or replace the implant.
The following are some signs and symptoms that an implant placement has been unsuccessful:
- the implant is excessively mobile
- pus or other secretions come from the site
- pain when tapping the implant
- rapid, progressive bone loss
Each person is likely to have a different experience of dental implant surgery. Factors that may influence this include:
- the number of teeth requiring replacement
- the location of the implants within the jaw
- the quality and quantity of bone at the implant site
- the person’s underlying oral and systemic health
Depending on these factors, additional procedures may be necessary. These can include:
Sinus augmentation
Placing an implant in the upper jawbone is usually difficult because of the location of the sinuses.
The surgeon may need to perform a sinus augmentation — a procedure to lift the floor of the sinuses to allow more bone to develop so that the implantation can be successful.
Ridge modification
Some people have a jawbone abnormality that prevents enough bone for an implant from developing. In such cases, a surgeon may need to perform a ridge modification.
This involves lifting the gum to expose the area of deformed bone. The surgeon will then use a bone or bone substitute to repair and build up the area. This improves the quality of the jawbone in preparation for dental implant surgery.
After a person has undergone dental implant surgery, they must continue to brush and floss their teeth regularly. Artificial teeth require the same care and maintenance as regular teeth.
The surgeon or dentist will also schedule follow-up visits to monitor the implants and make sure that the teeth and gums are healthy. It is important to return to the dentist every 6 months for professional cleanings.
The cost of dental implant surgery varies, and the following factors can influence it:
- the number and types of implants required
- the location of the implants within the jaw
- whether there is a need for any additional procedures to prepare the mouth for surgery
A dentist or another oral health professional can estimate the cost of dental implant surgery during an initial examination.
Some dental insurance policies cover a larger portion of the cost.
Other tooth replacement options, such as bridges, may be less expensive. However, bridges are harder to keep clean and often require replacement and repair, increasing the overall cost. Dental implants may provide longer-term benefits if a person takes care of them well.
Dental implants are fixtures in the bone that replace missing teeth. Implants have a high success rate and can provide long-term benefits.
Some people need additional procedures to prepare their mouth for dental implants. These will add to the overall cost. The number and type of implants required can also raise the cost.
Anyone considering dental implant surgery should ask their dentist whether it is right for them.
Source link
 Black America Breaking News for the African American Community
Black America Breaking News for the African American Community